Burden of Acute Respiratory Illness among Healthcare Workers in Kenya
BoARI Study
Study Duration
24 months
2023 – 2025
Project Locations
12 counties
500 locations
Lead Researchers
Prof. Kariuki Njenga – WSU
Dr. Nancy Otieno – KEMRI
Dr. Gideon Emukule – CDC
Study Participants
Healthcare Workers
Background & Rationale
Acute respiratory illnesses (ARIs) are diseases of the respiratory system that are of sudden onset (history of ≤10 days). Symptoms include – cough (new or worsening cough), runny nose, sore throat, shortness of breath, and chills or hotness of the body. The ARIs are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality; and the overall burden of disease based on disability-adjusted life years (DALY). Common causes include viruses (influenza, RSV, rhinoviruses, adenovirus, coronaviruses, etc.), bacteria (S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, S. aureus, etc.), and environmental agents (air pollution, smoking etc.). Children aged <5 years, pregnant women, elderly, and comorbid persons have an increased risk of severe ARI outcomes. Healthcare workers (HCWs) are at a higher risk of exposure to ARIs compared to the general population. HCWs may also transmit these ARIs to their patients, colleagues, and social networks.
The most common occupational infections of concern among HCWs are viral respiratory infections (influenza, coronaviruses, etc.), tuberculosis, and hepatitis B and C.
This study focusses on viral ARIs due to their high transmissibility, severe outcomes among those vulnerable, challenges with diagnostics and therapies. Further, limited data exists on the burden of ARIs among HCWs. In 2016, Kenya Immunization Technical Advisory Group (KENITAG) found little data to support proposals for HCWs flu vaccination.
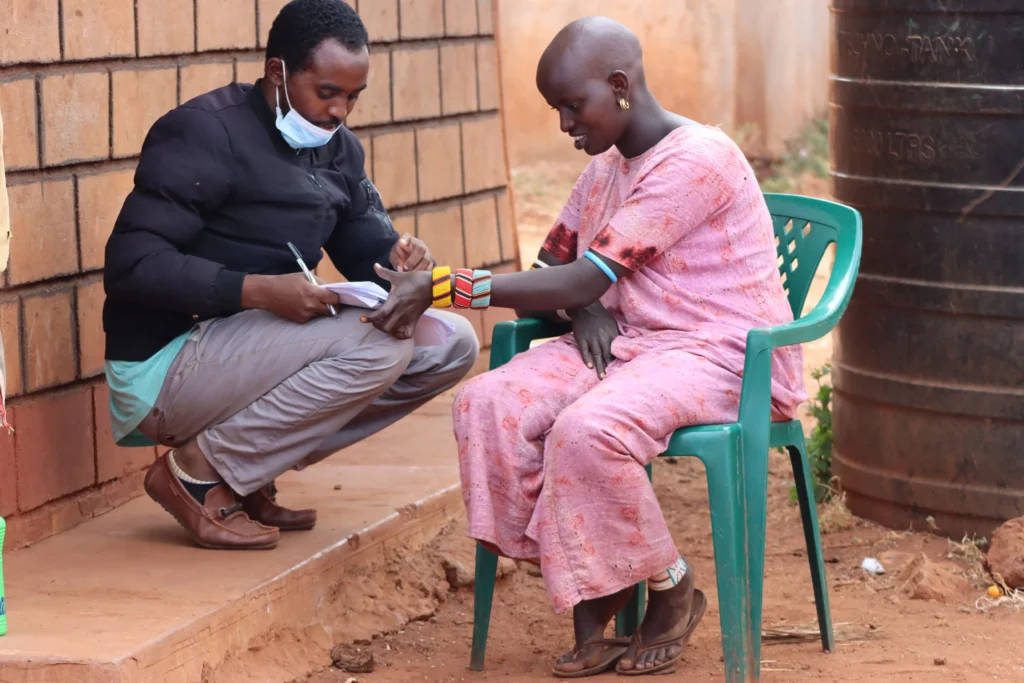

Study Objectives
Objective I
Estimating the annual incidence of ARI associated with influenza, SARS-CoV-2, RSV, and other respiratory viral pathogens among HCWs
Objective II
Determining factors associated with incidence and severity of pathogen and non-pathogen specific ARI among HCWs
Objective III
Estimating the economic costs associated with ARIs among HCWs
Objective IV
Describing healthcare seeking practices among HCWs with ARIs
Determining the immune responses and kinetics of infection by influenza, SARS-CoV-2, RSV, and other respiratory viral pathogens among HCWs
Methodology Overview
The study employs a pragmatic cluster-randomized design integrated within routine immunization systems to ensure real-world applicability and scalability.
Study Areas & Cluster Selection
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Implementation Approach
Integration Within National Systems
Funder

Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
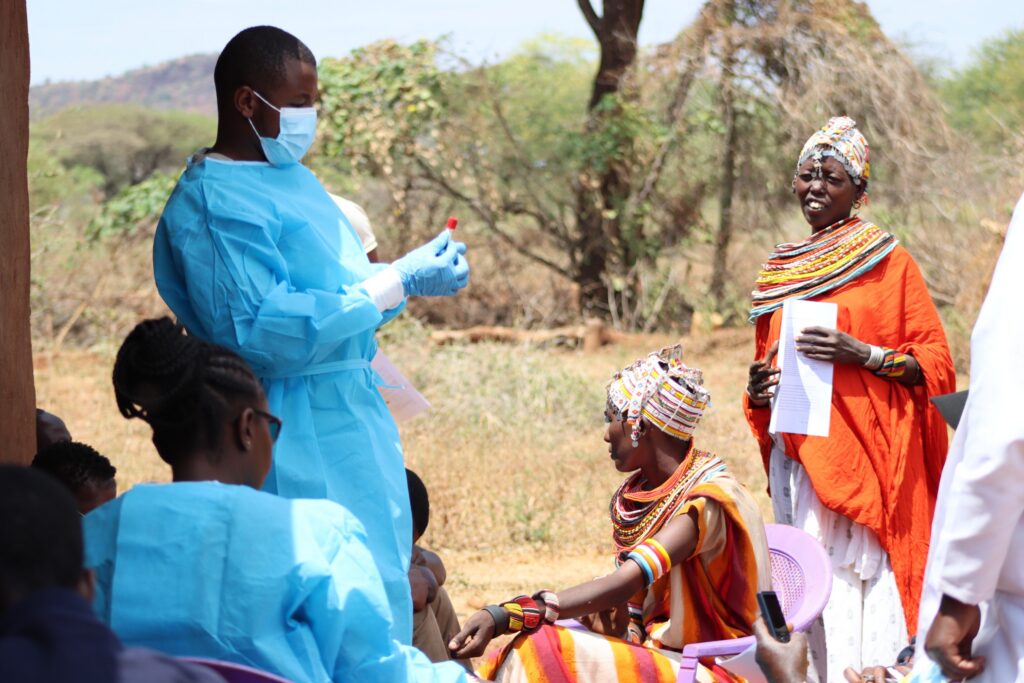
Media & Visual Evidence
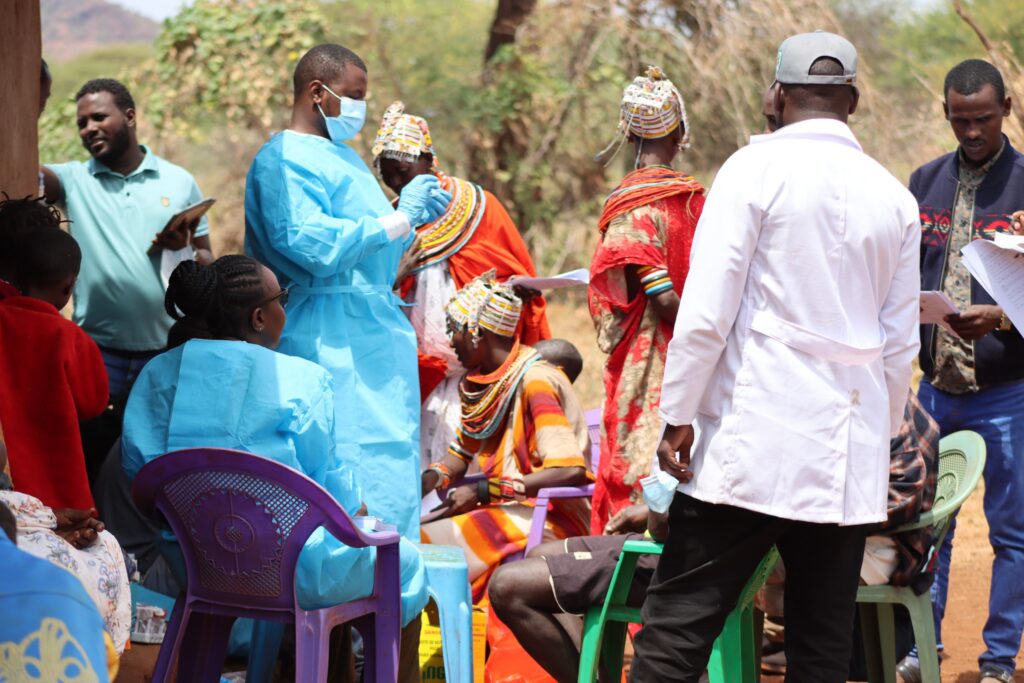

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
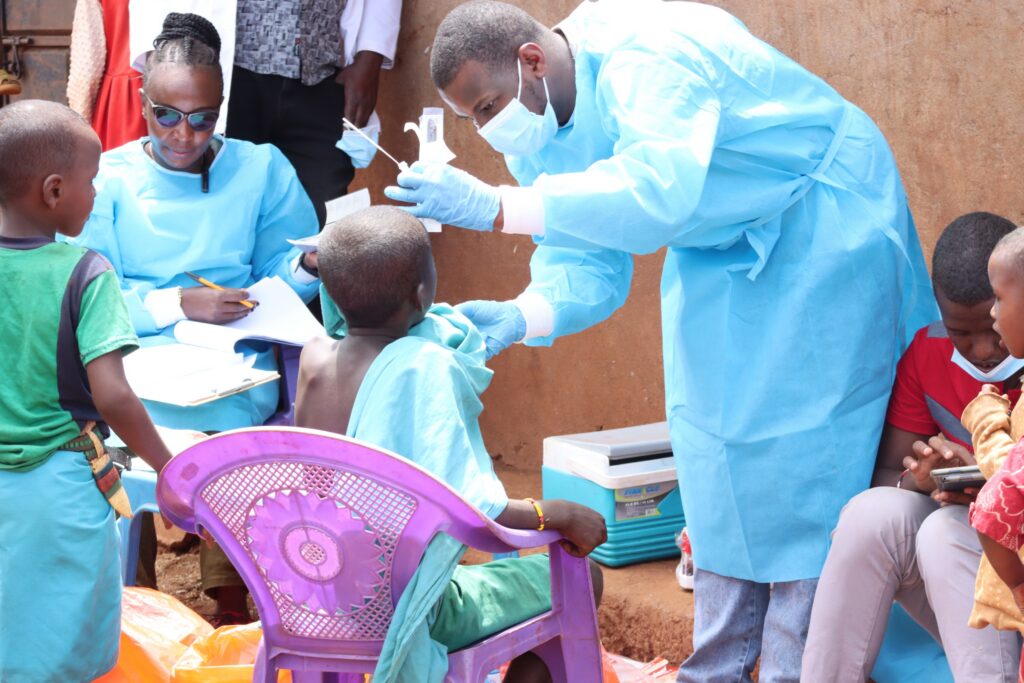
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
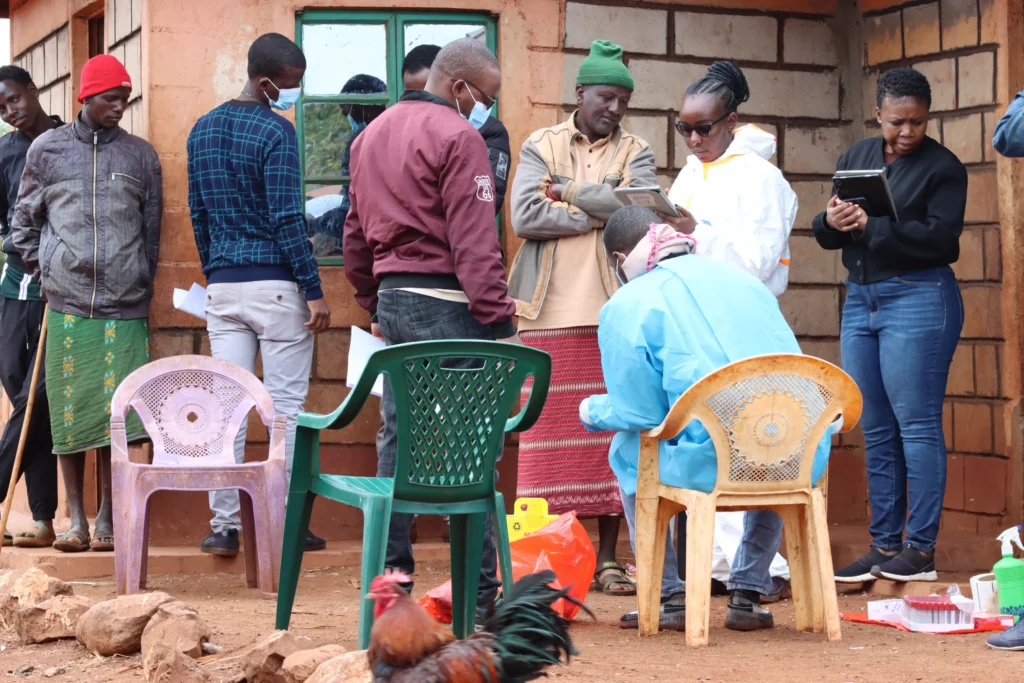

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
